Introduction
Express.js, commonly known as Express, is one of the most widely used web application frameworks for Node.js. It simplifies the development of web applications and APIs by providing a robust set of tools for handling HTTP requests, responses, routing, and middleware. This deep dive into Express will explore its core functionalities, configuration, middleware concepts, routing mechanisms, error handling, performance optimization, security practices, and deployment strategies. By the end, you should have a comprehensive understanding of how to build scalable, efficient, and secure applications using Express.
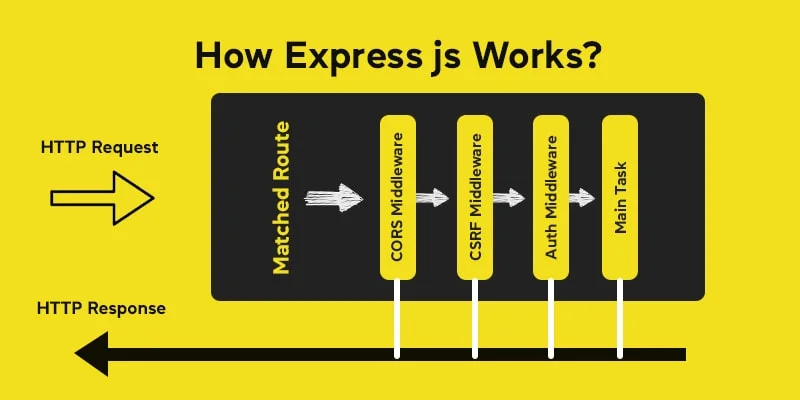
1. Overview of Express.js
Express.js was developed as a minimalistic framework that enhances the functionality of Node.js by adding features suited for web and API development, making it easier to handle complex backend operations.
1.1 Key Features of Express.js
- Minimal and Unopinionated: Express provides flexibility, allowing developers to choose how they structure their applications.
- Middleware Support: Easily integrates third-party middleware to extend its functionality.
- Robust Routing System: Supports various HTTP methods and routing mechanisms, enabling complex URL handling.
- Template Engines Support: Provides tools for rendering dynamic HTML pages using template engines like EJS, Pug, and Handlebars.
- Extensibility and Scalability: Highly adaptable to handle small applications or scale up to more complex architectures.
2. Installation and Basic Setup
Getting started with Express requires minimal setup. Assuming Node.js and npm are installed, follow these steps to set up a basic Express project:
2.1 Project Structure
A typical Express application might have the following structure:
2.2 Creating a Simple Server
The following code demonstrates a simple Express server setup:
3. Middleware in Express
Middleware functions in Express can execute code, modify the request/response objects, end the request-response cycle, or pass control to the next function in the stack.
3.1 Built-in Middleware
Express provides several built-in middleware functions like express.json() for parsing JSON and express.static() for serving static files.
3.2 Custom Middleware
Custom middleware functions are easy to create. Here’s a simple logger middleware:
3.3 Third-party Middleware
Popular third-party middleware includes:
- body-parser: Parses incoming request bodies.
- cookie-parser: Parses cookies.
- morgan: HTTP request logger.
To use these, install the packages with npm and integrate them as follows:
4. Routing in Express
Routing is the process of determining how an application responds to client requests to specific endpoints.
4.1 Basic Routing
4.2 Route Parameters
Express routes can handle dynamic parameters in the URL:
4.3 Route Grouping with Express Router
Grouping related routes using Express Router helps organize the application:
5. Error Handling
Error handling in Express involves defining middleware functions that process errors passed through the application.
Express identifies an error-handling middleware by its signature, which must have four parameters: err, req, res, and next.
5.1 Creating Custom Error Handlers
Custom error classes allow for more structured error handling:
6. Handling Requests and Responses
Express makes handling HTTP requests and responses straightforward by providing various methods to read from and send data back to the client.
6.1 Request Object
Express’s req object provides details about the HTTP request, such as parameters, query strings, headers, and the request body.
6.2 Response Object
The res object allows us to send data back to the client in various formats.
7. Templating with Express
Express supports various template engines, including Pug, EJS, and Handlebars.
7.1 Setting Up a Template Engine
8. Database Integration
Express can integrate with databases like MongoDB, PostgreSQL, and MySQL.
8.1 MongoDB with Mongoose
To use MongoDB, install Mongoose:
Set up a Mongoose connection in your Express app:
Define a simple schema and model:
9. Security Best Practices
Securing an Express application requires following certain best practices:
9.1 Helmet
Helmet helps secure Express apps by setting various HTTP headers:
9.2 HTTPS Enforcement
Ensure that your app is only accessible over HTTPS, which can be handled with middleware.
9.3 Data Sanitization
Prevent NoSQL injection and XSS attacks by sanitizing user input, commonly achieved with packages like express-validator.
10. Performance Optimization
Improving the performance of an Express application can involve caching, compression, and efficient routing.
10.1 Compression Middleware
10.2 Caching
Use caching mechanisms such as Redis for storing frequently accessed data and reducing database calls.
10.3 Load Balancing
For large applications, implement load balancing strategies to distribute requests across multiple servers.
11. Testing in Express
Testing Express applications ensures reliability and helps catch errors early.
11.1 Unit Testing with Mocha and Chai
Set up simple tests in a file named test.js:
12. Deployment
12.1 Deploying with Heroku
Heroku provides a simple platform for deploying Node.js applications.
- Initialize a Git repository and commit the code.
- Create a Heroku app with
heroku create. - Push the code to Heroku with
git push heroku main.
12.2 Dockerizing Express Applications
To run an Express app as a Docker container, create a Dockerfile:
Conclusion
Express.js serves as a powerful, flexible, and efficient framework for building web applications and APIs in Node.js. From setting up a server to deploying a production-grade application, Express provides all the tools necessary for developing scalable applications. By following best practices for security, optimizing performance, and ensuring thorough testing, you can create Express applications that are reliable and resilient in production environments.
More Informations

In delving into the multifaceted realm of Express, an extensively utilized and dynamically evolving web application framework for Node.js, it becomes imperative to embark on a comprehensive exploration of its origins, core functionalities, architectural nuances, and the myriad applications that have been shaped by its adept capabilities.
Express, a minimalist and unopinionated framework, stands as a foundational component within the Node.js ecosystem, seamlessly facilitating the development of robust and scalable web applications. Its inception can be traced back to 2010 when TJ Holowaychuk initially conceptualized and released it as a lightweight alternative to the then-prevailing web frameworks. Since its introduction, Express has garnered widespread adoption and commendation within the development community, emerging as a de facto standard for constructing server-side applications in Node.js.
At its essence, Express operates as a middleware-oriented framework, enabling developers to design and structure their applications through the integration of modular middleware components. These middleware modules serve as intermediaries between the incoming HTTP request and the corresponding server response, affording developers a high degree of flexibility in crafting the flow and functionality of their applications. This distinctive middleware-centric approach distinguishes Express, fostering a modular and extensible architecture that can be tailored to meet the specific requirements of diverse projects.
A pivotal facet of Express lies in its ability to streamline the creation of robust APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) by providing a succinct and expressive syntax. The framework facilitates the routing of HTTP requests to designated handler functions, allowing developers to encapsulate the logic associated with specific endpoints. This routing mechanism empowers the creation of RESTful APIs, adhering to the principles of Representational State Transfer (REST), a prevalent architectural style in modern web development.
Express further bolsters its versatility through the incorporation of a templating engine, enabling the dynamic generation of HTML content. Widely adopted engines like EJS (Embedded JavaScript) and Pug seamlessly integrate with Express, facilitating the rendering of dynamic views based on data provided by the server. This capacity for dynamic content generation positions Express as a potent tool for crafting not only APIs but also rendering server-side views for web applications.
In the realm of middleware, Express encompasses a diverse array of modules, each catering to distinct aspects of web application development. Middleware functions may encompass tasks such as logging, authentication, and error handling, affording developers the means to modularize and organize their codebase effectively. This modular approach not only enhances code maintainability but also contributes to the scalability and extensibility of Express applications.
In the sphere of connectivity, Express seamlessly integrates with databases, leveraging a plethora of middleware and plugins to interface with databases like MongoDB, MySQL, and PostgreSQL. This integration facilitates the establishment of robust data-driven applications, where Express serves as the conduit between the frontend and the backend data stores.
The extensibility of Express is further underscored by the vibrant ecosystem of third-party middleware and plugins available through the Node Package Manager (NPM). Developers can augment their Express applications with a diverse array of functionalities, ranging from authentication mechanisms and session management to compression and caching strategies. This expansive ecosystem empowers developers to tailor their applications with precision, drawing from a rich repository of community-contributed modules.
Asynchronous programming, a fundamental paradigm in Node.js, seamlessly integrates with Express, allowing developers to harness the non-blocking I/O capabilities inherent in Node.js. This concurrency model, underpinned by the event-driven architecture of Node.js, enables Express to efficiently handle a large number of concurrent connections, ensuring optimal performance in scenarios characterized by high traffic and real-time interactions.
Moreover, Express does not exist in isolation; it is often employed in conjunction with other technologies to construct comprehensive web stacks. Commonly, developers pair Express with front-end frameworks like React or Angular to create full-stack applications, encompassing both the server-side and client-side components. This collaborative synergy between Express and front-end frameworks exemplifies the versatility and adaptability of the framework within diverse development paradigms.
In the ever-evolving landscape of web development, the longevity and resilience of Express are testament to its enduring relevance and efficacy. Despite the emergence of alternative frameworks and technologies, Express maintains its standing as a stalwart choice for developers seeking a robust, flexible, and scalable platform for building web applications. Its minimalist design philosophy, coupled with a wealth of features and a thriving community, positions Express as a cornerstone in the architectural foundation of modern web development, embodying the ethos of simplicity, modularity, and performance.



