Rough Skin Patches: Causes, Treatments, and Prevention Strategies
The appearance of rough skin patches on various parts of the body is a common dermatological issue that can cause discomfort, self-consciousness, and even health complications if left untreated. These patches often indicate underlying skin issues or can sometimes be signs of broader health problems. Identifying the root causes and understanding effective treatment methods can help in managing or even preventing the condition. This article explores the primary causes, treatment options, home remedies, and preventive measures associated with rough skin patches.
Understanding Rough Skin Patches
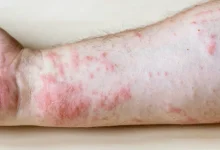
Rough patches on the skin often feel dry, scaly, and slightly raised, and they can appear in different forms depending on the underlying cause. While these patches can be harmless, they sometimes signal serious dermatological conditions that require medical attention. Common locations include elbows, knees, feet, and hands, though patches can appear on any part of the body.
Common Causes of Rough Skin Patches
-
Dry Skin (Xerosis)
- Description: One of the most common causes of rough skin is simply dry skin, also known as xerosis. When the skin loses moisture, it can become dry, cracked, and rough.
- Causes: Cold or dry climates, low humidity, overexposure to hot water, and harsh soaps are common contributors.
- Symptoms: Flaky, rough texture, and sometimes itchiness.
-
Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis)
- Description: Eczema is a chronic condition characterized by inflamed, itchy, and rough patches. It is common among both children and adults.
- Causes: Genetics, immune system dysfunction, and environmental triggers such as allergens or stress.
- Symptoms: Red, itchy, rough patches that may ooze or bleed when scratched.
-
Psoriasis
- Description: Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease that leads to the rapid buildup of skin cells, forming scales and red patches that are often itchy and painful.
- Causes: Overactive immune response that triggers skin cell proliferation.
- Symptoms: Silver, scaly, raised patches, commonly found on the scalp, elbows, and knees.
-
Keratosis Pilaris
- Description: Often called “chicken skin,” keratosis pilaris appears as small, rough bumps, typically on the upper arms, thighs, cheeks, and buttocks.
- Causes: Buildup of keratin, a protein that protects the skin, which blocks the hair follicles.
- Symptoms: Painless, small, rough bumps, often more noticeable in cold, dry weather.
-
Actinic Keratosis
- Description: Caused by long-term sun exposure, actinic keratosis is a precancerous condition that appears as rough, scaly patches, usually on sun-exposed areas like the face, hands, and neck.
- Causes: Chronic UV exposure.
- Symptoms: Rough, scaly patches that can be red or brown and may feel itchy or tender.
-
Ichthyosis
- Description: Ichthyosis is a group of genetic skin disorders characterized by dry, scaly skin that may resemble fish scales.
- Causes: Genetic mutations affecting skin cell turnover.
- Symptoms: Thick, dry, and scaly skin, often present from birth or early childhood.
Treatments for Rough Skin Patches
Medical Treatments
-
Topical Steroids: Prescribed for inflammatory conditions like eczema and psoriasis, these creams reduce inflammation and itchiness. However, they should be used under medical supervision due to potential side effects with prolonged use.
-
Retinoids: Often used for keratosis pilaris and severe cases of psoriasis, retinoids help in skin cell turnover, which reduces the buildup of dead cells. They can be effective in smoothing out rough patches but may cause irritation in sensitive skin.
-
Moisturizers with Urea or Lactic Acid: These ingredients help to soften and exfoliate the skin, especially effective for conditions like ichthyosis and keratosis pilaris, where thickened skin is a concern.
-
Phototherapy: This is a treatment option for psoriasis and eczema that involves exposing the skin to controlled amounts of natural or artificial light, which can reduce inflammation and slow down skin cell turnover.
-
Cryotherapy for Actinic Keratosis: In cases of actinic keratosis, cryotherapy or freezing off the lesions with liquid nitrogen is a common treatment to prevent potential progression to skin cancer.
Over-the-Counter and Prescription Moisturizers
Maintaining moisture levels in the skin is crucial in managing rough patches. Some effective ingredients in OTC and prescription moisturizers include:
- Ceramides: These lipids restore the skin barrier.
- Hyaluronic Acid: It retains moisture, making the skin appear smoother and less dry.
- Glycerin: A humectant that draws moisture into the skin, helping to smooth rough areas.
Home Remedies for Rough Skin Patches
-
Coconut Oil: Known for its moisturizing properties, coconut oil can be applied to dry skin to restore hydration and smooth rough patches. Its natural fatty acids help repair the skin barrier.
-
Aloe Vera Gel: Aloe vera is highly hydrating and has anti-inflammatory properties that soothe and repair irritated skin. It can be particularly helpful for eczema and sun-exposed skin.
-
Oatmeal Baths: Adding finely ground oatmeal to a bath can soothe itching and reduce inflammation. Oatmeal contains compounds that have anti-inflammatory properties, providing relief for eczema and psoriasis.
-
Honey and Olive Oil Mask: A combination of honey and olive oil provides antioxidants and deep hydration, suitable for rough patches on the face and hands. Honey’s antimicrobial properties make it an excellent choice for sensitive skin types.
-
Apple Cider Vinegar: Diluted apple cider vinegar can help balance the skin’s pH and has mild exfoliating properties. However, it should be used with caution, especially on sensitive skin.
-
Sugar Scrubs: Regular exfoliation with sugar and honey can help remove dead skin cells and smooth rough patches. However, scrubs should be used sparingly to avoid further irritation.
Lifestyle Changes and Preventive Measures
-
Regular Moisturization: Applying a rich moisturizer daily, especially after bathing, helps lock in moisture and prevents the skin from drying out. Look for products containing ceramides, urea, and hyaluronic acid.
-
Hydration: Staying hydrated is essential for skin health. Drinking adequate water keeps the skin hydrated from within and helps maintain elasticity.
-
Avoiding Harsh Soaps and Detergents: Harsh soaps strip the skin of its natural oils, exacerbating dryness and roughness. Opt for mild, fragrance-free cleansers and avoid scrubbing the skin too vigorously.
-
Humidifier Usage: Using a humidifier during dry seasons, especially winter, can help maintain skin moisture levels and prevent the skin from drying out due to low humidity.
-
Sun Protection: Applying a broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher can prevent sun damage, reducing the risk of actinic keratosis and other sun-related skin issues.
-
Gentle Exfoliation: Regular but gentle exfoliation helps remove dead skin cells that accumulate on the surface, giving the skin a smoother texture. Avoid over-exfoliating, which can irritate the skin and worsen rough patches.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If rough patches are persistent, spreading, or accompanied by symptoms like pain, oozing, or significant itching, it’s best to consult a dermatologist. Early diagnosis and intervention can help manage chronic conditions and rule out any potential skin cancers. Additionally, for conditions like actinic keratosis, early treatment can prevent progression to squamous cell carcinoma.
Table: Overview of Common Causes and Treatments of Rough Skin Patches
| Condition | Causes | Symptoms | Treatment Options |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dry Skin (Xerosis) | Low humidity, harsh soaps | Flaky, rough texture | Moisturizers with ceramides, lactic acid |
| Eczema | Genetics, allergens | Red, itchy, inflamed patches | Topical steroids, emollients |
| Psoriasis | Autoimmune response | Scaly, raised, red patches | Phototherapy, retinoids, topical steroids |
| Keratosis Pilaris | Keratin buildup | Small, rough bumps | Moisturizers with urea, gentle exfoliants |
| Actinic Keratosis | Sun exposure | Rough, scaly patches on sun-exposed areas | Cryotherapy, topical treatments |
| Ichthyosis | Genetic mutation | Thick, scaly skin | Urea-based creams, exfoliation |
Conclusion
Rough skin patches are not only a cosmetic concern but also a potential indicator of underlying health issues. Understanding the causes, treatments, and preventive strategies is essential for maintaining healthy, smooth skin. Whether due to environmental factors, genetics, or immune system responses, these patches can be managed through a combination of medical treatments, lifestyle changes, and natural remedies. By addressing the issue proactively and seeking medical advice when needed, individuals can effectively control rough skin patches and maintain overall skin health.