Understanding the Significance of Email Delegation in Microsoft Outlook
In the rapidly evolving domain of electronic communication, managing a flood of emails efficiently and securely remains paramount for both individual professionals and organizational teams. Microsoft Outlook, as one of the leading email management platforms, has integrated a robust feature known as email delegation—an instrument designed to facilitate seamless collaboration, streamline workflows, and distribute responsibilities within digital ecosystems. This process empowers individuals to authorize others to access, respond to, and manage their email accounts on their behalf, thereby enhancing productivity and fostering a collaborative environment.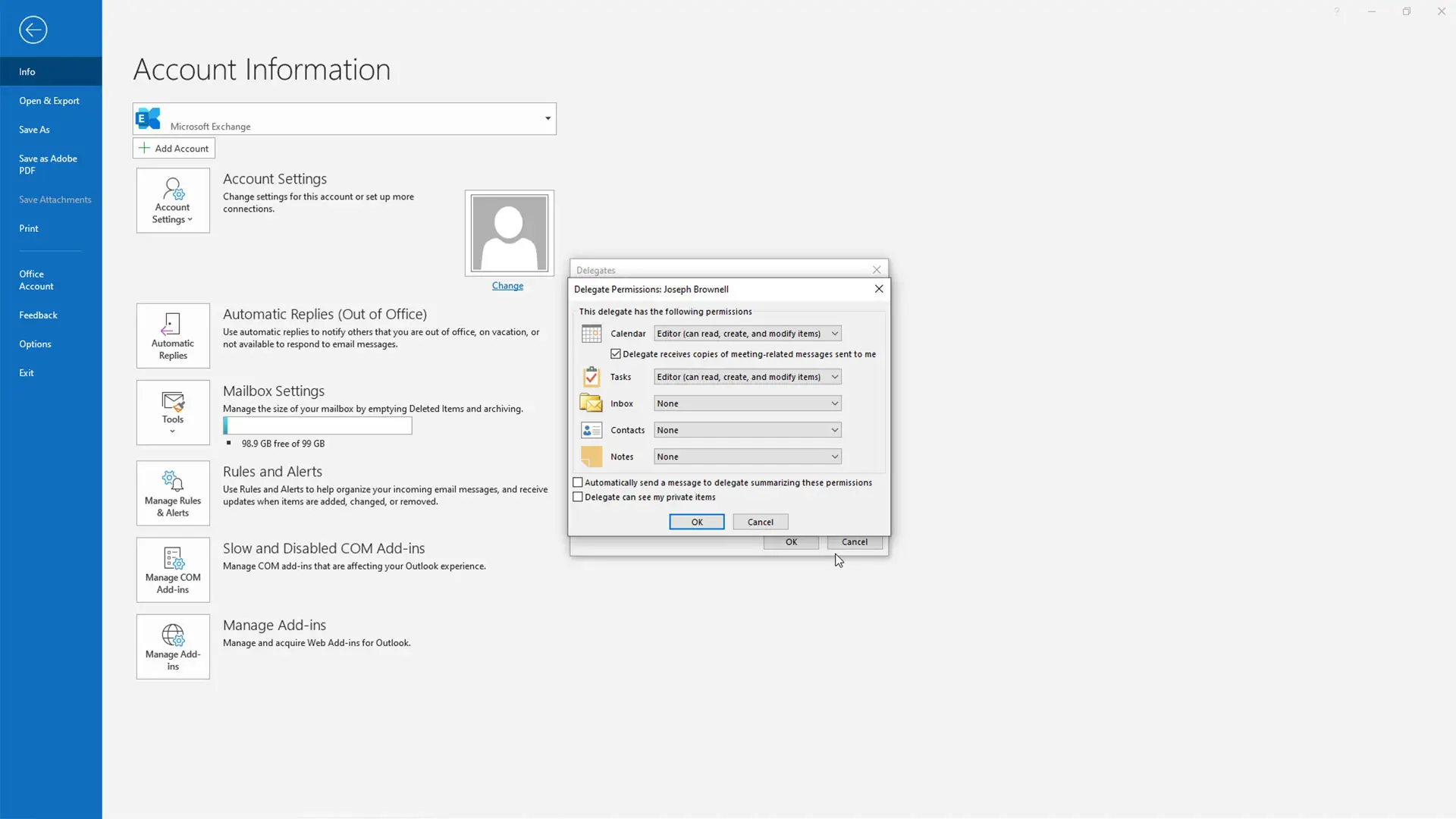
The decision to delegate email responsibilities is often driven by varied operational needs: an executive may delegate to an assistant to handle routine correspondence; a team leader might assign mailbox management to a trusted colleague; or individuals may entrust family members with access during emergencies or extended absences. Such arrangements secure a blend of trust and strategic collaboration necessary in modern digital communications, with the delegation process carefully crafted to suit diverse roles and privacy considerations. Recognizing the nuances within this feature is critical; a misstep can compromise data security or blur accountability, underscoring the importance of detailed procedural understanding. This comprehensive exploration, published on freesourcelibrary.com, aims to delineate the intricacies of email delegation across various versions of Microsoft Outlook, providing in-depth insights, technical steps, and contextual considerations to optimize its use.
Fundamental Concepts and Core Principles of Email Delegation
What Is Email Delegation?
At its essence, email delegation entails granting a designated individual, known as a delegate, permission to access, manage, and respond to incoming emails within a user’s mailbox. This comprehensive permission framework allows for certain levels of control, ranging from simply viewing messages to composing, replying, and managing email folders on behalf of the account owner. The delegate operates within the bounds of assigned permissions, actively representing or managing the mail account based on the scope specified by the delegator.
The Rationale Behind Delegating Emails
Delegation serves multiple practical purposes. In professional settings, managers and executives delegate to assistants who handle scheduling, respond to inquiries, and manage correspondence, thereby optimizing operational efficiency. Beyond efficiency, this arrangement also enhances responsiveness, especially when the primary user is unavailable or overwhelmed with tasks.
In personal contexts, delegation might involve sharing access with trusted family members or friends during travel, illness, or absence, ensuring continuity in communication management. Furthermore, for individuals managing complex or multiple email accounts, delegation supports better organization and prioritization, preventing vital messages from being overlooked.
Legal and Ethical Dimensions of Email Delegation
While delegation fosters collaboration, it simultaneously raises concerns regarding data privacy, confidentiality, and security. The act of granting access implicitly involves sharing sensitive information. It necessitates clear boundaries, mutual trust, and well-defined permissions. Organizations must implement policies that safeguard privacy, ensuring that delegates act responsibly, respecting boundaries, and understanding the scope of their authority.
Technical Foundations of Outlook Email Delegation
Variation Across Outlook Platforms and Versions
The deployment of email delegation differs across various versions of Outlook, including Outlook for the web (OWA), Outlook 2016, Outlook 2019, and Outlook in Microsoft 365. Each platform exhibits unique navigation paths, feature sets, and permission granularity, necessitating tailored procedural knowledge.
Outlook for the Web (OWA)
In Outlook for the web, the process hinges on navigating through a simplified interface with clear directives. The user initiates the procedure via the Settings menu, typically accessible through a gear icon located at the top right corner. Once inside the Settings, the user searches for “View all Outlook settings,” narrowing down to the ‘Mail’ section, then to ‘Accounts,’ and finally to ‘Grant access’ or ‘Manage Delegates.’ This pathway offers a user-friendly environment, suitable for quick setup and management of delegation rights.
Outlook Desktop Applications (2016, 2019, Microsoft 365)
In desktop versions, the process is embedded within the broader Outlook interface, accessible via the ‘File’ tab on the Ribbon. From there, users navigate through ‘Account Settings’ and ‘Delegate Access.’ Clicking ‘Add’ reveals a dialog box where email addresses can be entered, after which permission levels are selected. This granular control accommodates complex organizational workflows and varied permission needs.
Key Permissions and Their Implications
| Permission Type | Description | Common Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Full Access | Complete control over the mailbox, including opening and managing all folders, sending, and receiving emails. | Administrative roles or dedicated assistants with comprehensive authority. |
| Send on Behalf | Allows the delegate to send emails as if on behalf of the owner, with the email displaying “on behalf of” authority. | Executive assistants managing correspondence on behalf of executives. |
| Editor | Permission to read, create, modify, and delete items within mailbox folders. | Collaborative team projects or shared team inboxes. |
| Reviewer | Read-only access; no modification permissions. | Audit or review tasks, access to monitor external communications. |
| Author | Ability to read and create items, but not delete or modify existing messages. | Delegates responsible for initial message drafting. |
The Step-by-Step Process for Delegation in Various Outlook Versions
Outlook for the Web
Step 1: Access the Settings Menu
Begin by clicking on the gear icon located at the top right corner of the Outlook Web interface. From the dropdown menu, select “View all Outlook settings” to access the comprehensive settings panel.
Step 2: Navigate to Mail and Delegation Settings
In the settings panel, select “Mail,” then under the submenu, locate and click on “Accounts” or “Delegates,” depending on the version. The ‘Grant access’ or ‘Manage delegates’ option appears here.
Step 3: Add a Delegate
Click on “Add people” or “Add a delegate,” and enter the email address of the person you wish to authorize. Assign specific permissions—such as “Can read and manage my email” or “Send on behalf of”—tailoring their authority scope.
Step 4: Confirm and Notify
Finalize the process by clicking “Save” or “Add,” which triggers an email notification to the delegate informing them of their new responsibilities. Depending on organizational policies, additional confirmation might be required.
Outlook 2016, 2019, and Microsoft 365 Desktop
Step 1: Access Account Settings
Select the ‘File’ tab, then click on ‘Account Settings’ followed by ‘Delegate Access.’ This section is central to managing delegation permissions.
Step 2: Manage Delegates
Click on ‘Add’ to select a contact or type the email address of the delegate. Then, configure permissions such as ‘Editor,’ ‘Reviewer,’ or ‘Full Access,’ based on the role required.
Step 3: Set Permissions
Specify whether the delegate can see private items, send emails on your behalf, or manage your mailbox fully. These granular controls ensure role-specific authorization aligned to organizational needs.
Step 4: Finalize and Notify
Click ‘OK’ or ‘Apply’ to set the permissions. The delegate receives a system notification, and the setup completes with the delegated authority now active.
Implications and Best Practices of Email Delegation
Balancing Trust and Security
Delegation is fundamentally a trust-based arrangement. Selecting the right delegate involves assessing their reliability, discretion, and understanding of privacy boundaries. Organizations should establish clear protocols and signed agreements, especially when sharing sensitive or confidential information.
Security Considerations and Data Privacy
Granting access to email accounts naturally raises privacy concerns, particularly concerning sensitive content and personal data. Implementing security measures such as multi-factor authentication, periodic audits of delegate activities, and setting expiration dates on delegations can mitigate risks.
Legal and Compliance Aspects
In regulated environments, delegation practices must adhere to legal frameworks like GDPR or HIPAA, ensuring compliance regarding data handling and privacy policies. Transparency in delegation procedures and maintaining thorough logs is essential for accountability.
Managing and Monitoring Delegation
Effective management entails regular review of delegate permissions, adjusting or revoking access as needed, and establishing clear communication channels for updates or concerns. Training delegates on ethical standards and organization policies ensures responsible stewardship.
The Broader Context: Delegation as Digital Estate Planning
Beyond immediate operational benefits, email delegation forms a part of comprehensive digital estate planning, preparing individuals and organizations for contingencies such as emergencies, retirement, or estate transfer. Ensuring that trusted persons can manage digital assets aligns with holistic digital lifecycle management, including the handling of emails, files, social media accounts, and more.
Platform Dynamics and the Future of Email Delegation
Technological Evolution and Security Enhancements
Microsoft continually advances Outlook’s capabilities, integrating features such as enhanced permissions, audit logs, and granular access controls, to improve security and usability. Features like Microsoft’s ‘Microsoft Information Protection’ enable organizations to classify and safeguard email content even in shared access scenarios.
Emerging Trends and Implications
Artificial intelligence and machine learning will influence delegation practices by automating routine email management, recognizing delegation needs dynamically, and providing smarter permission management. Upcoming platforms are expected to incorporate more seamless, secure, and customizable delegation workflows.
Conclusion: Navigating the Complex Landscape of Email Delegation
Mastering email delegation within Microsoft Outlook necessitates a comprehensive understanding of technological steps, permission intricacies, and contextual implications. It embodies a strategic tool for enhancing efficiency, fostering collaboration, and managing digital assets responsibly. As the digital environment evolves, staying informed about platform updates, security best practices, and legal standards becomes indispensable for leveraging delegation optimally. Whether in professional domains or personal scenarios, the effective use of email delegation can significantly streamline communication workflows while safeguarding trust and confidentiality.
For further detailed guides and updates on Outlook features, visit freesourcelibrary.com.
References
- Microsoft Support Documentation: https://support.microsoft.com
- ISO/IEC 27001 Information Security Management Standards
