Population of Qatar: A Comprehensive Overview
Qatar, a small but influential country in the Arabian Peninsula, has witnessed rapid economic growth and transformation over the past few decades. With a strategic location, a rich cultural heritage, and one of the highest GDPs per capita in the world, Qatar has become a hub of international business, culture, and sports. Understanding the demographics and population structure of Qatar is crucial for anyone interested in the country’s socioeconomic landscape. This article aims to provide a detailed analysis of Qatar’s population, including its size, growth trends, composition, and the factors influencing these developments.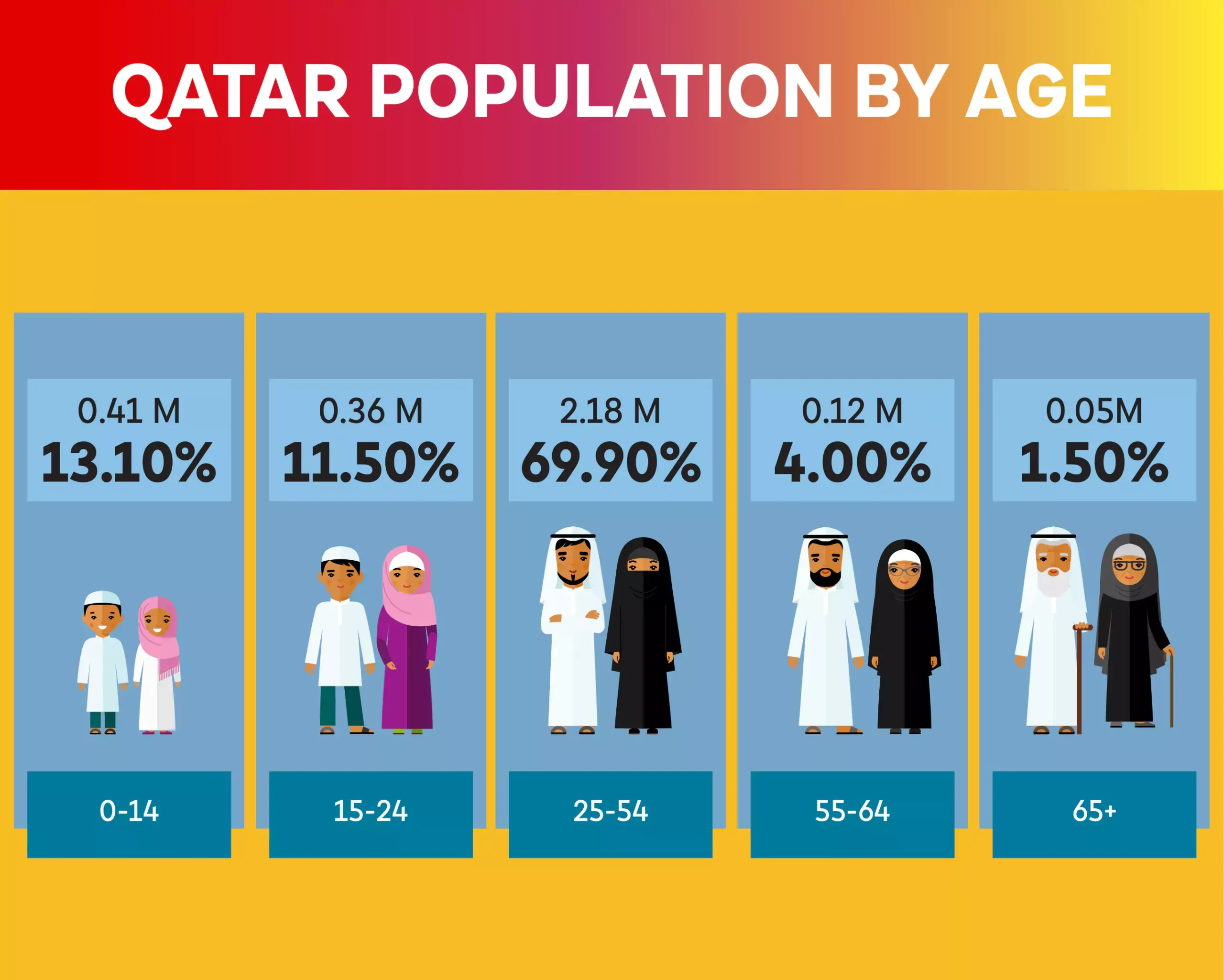
Historical Context and Population Growth
Historically, Qatar’s population was relatively small and consisted mostly of Bedouin tribes. The country was primarily dependent on pearl diving, fishing, and trade, and the population remained sparse due to the harsh desert environment. It wasn’t until the discovery of oil and natural gas reserves in the mid-20th century that the country experienced rapid development and urbanization. This shift transformed Qatar into one of the wealthiest nations in the world.
In 2025, Qatar’s population is estimated to be approximately 2.9 million people. This rapid increase in population can be attributed to several key factors, including the country’s oil and gas wealth, which has attracted a large influx of foreign workers. Qatar’s population growth rate has been one of the highest globally, with an average annual increase of about 3.5% over the past few years.
Population Composition: Nationals vs. Expatriates
One of the most unique aspects of Qatar’s population is the overwhelming proportion of expatriates. Qatar nationals, or Qataris, make up a relatively small percentage of the total population, constituting only about 12-15%. The remainder of the population—approximately 85-88%—consists of foreign nationals. This demographic composition is a result of Qatar’s labor force, which primarily relies on foreign workers from countries like India, Nepal, the Philippines, Bangladesh, and other nations in South Asia, as well as Western expatriates involved in business, finance, and technology sectors.
The large expatriate population has had a profound impact on the country’s culture, economy, and social fabric. While Qataris maintain a dominant role in the political, cultural, and economic spheres, the expatriates contribute significantly to the workforce, especially in industries such as construction, healthcare, hospitality, and education. The presence of expatriates also influences Qatar’s consumer market, driving demand for goods and services, particularly in sectors catering to foreign nationals.
Gender Distribution
The gender distribution in Qatar is notably skewed due to the high number of male expatriate workers, particularly in labor-intensive industries. Men represent approximately 75-80% of the population, while women make up the remaining 20-25%. This imbalance is primarily due to the demand for male workers in construction and infrastructure development projects, as well as the relatively small number of Qatari women in the labor force compared to their male counterparts.
However, it is important to note that Qatari women have been making significant strides in education and employment in recent years. The government has invested heavily in education for both men and women, and Qatar boasts one of the highest female literacy rates in the Arab world. Many Qatari women now work in various fields, including healthcare, education, and government, although they still make up a smaller proportion of the workforce than men.
Age Demographics
Qatar’s population is relatively young, with a median age of around 32 years. This youthful demographic is a result of the country’s growing economy, which has attracted young professionals and skilled workers from around the world. The population pyramid shows a large proportion of individuals in the working-age group, between 25 and 54 years old.
However, the population also includes a growing number of young people, as Qatari families tend to have relatively high birth rates compared to other Gulf countries. The government has actively promoted family-friendly policies, including financial incentives for families and increased support for women in the workforce. This has contributed to a slow but steady increase in the Qatari national population.
The elderly population in Qatar, while still a smaller segment compared to younger age groups, is steadily increasing as life expectancy rises due to advancements in healthcare. Qatar has one of the highest life expectancies in the Middle East, thanks to the availability of world-class medical services and a high standard of living.
Migration Patterns and Labor Force
Qatar’s population is highly dynamic due to its dependence on migrant labor. The country has one of the highest migration rates in the world, with tens of thousands of workers arriving annually to fill positions in various sectors. The migrant workforce is primarily made up of individuals from South Asia, but there is also a significant number of workers from the Arab world, Southeast Asia, and other regions.
In recent years, Qatar has been shifting towards more sustainable migration practices. The government has introduced reforms to improve labor conditions, such as the introduction of a minimum wage and a new contract system that allows workers to change employers. These reforms have been implemented as part of Qatar’s broader efforts to modernize its economy and improve the lives of its migrant workers.
Despite these improvements, the labor force remains largely temporary, as many workers come to Qatar for short-term contracts. This transient nature of the workforce means that the population fluctuates throughout the year, with significant increases during periods of high demand for construction projects or during major events like the FIFA World Cup 2022, which saw a spike in temporary workers arriving to help prepare the country for the event.
Urbanization and Major Population Centers
Qatar’s rapid urbanization has transformed it from a small, sparsely populated nation into a modern, high-tech state with a booming urban population. The capital city, Doha, is home to over 80% of the country’s total population and has become a thriving metropolis. The city has undergone extensive development in recent years, with towering skyscrapers, luxury hotels, shopping malls, and modern infrastructure that reflect the country’s economic prosperity.
Doha is the focal point of Qatar’s business, education, and cultural life. It is also the host of numerous international events, including conferences, sporting events, and exhibitions, further attracting both tourists and expatriates. Other major cities in Qatar include Al Rayyan and Al Wakrah, which are also experiencing rapid growth due to the expanding economy and the increasing demand for housing and services.
Challenges and Opportunities
While Qatar’s population growth presents numerous opportunities, it also poses challenges. One of the key issues is the country’s reliance on foreign workers, which has led to concerns about the long-term sustainability of its labor market and social integration. The government is working on diversifying the economy and increasing the number of skilled Qatari workers in various sectors, but this process is still ongoing.
Another challenge facing Qatar is the need to balance the rapid growth of its urban areas with environmental sustainability. The country’s harsh desert climate poses significant challenges for water conservation, waste management, and energy consumption. As Qatar continues to grow, it will need to invest in sustainable technologies and policies to ensure the well-being of its population and the preservation of its natural resources.
Conclusion
Qatar’s population continues to grow and evolve, driven by the country’s booming economy, the influx of foreign workers, and a young, dynamic demographic. While Qatar’s population is still relatively small compared to many other nations, the rapid growth it has experienced over the last few decades reflects the country’s emergence as a global economic powerhouse. The demographics of Qatar are unique, with a large expatriate population, a youthful workforce, and a rapidly expanding urban landscape. As Qatar continues to invest in infrastructure, education, and sustainable development, its population dynamics will undoubtedly play a key role in shaping the future of the nation.
Understanding Qatar’s population trends and composition is crucial for businesses, policymakers, and researchers alike, as it offers insights into the challenges and opportunities facing the country in the coming years. The future of Qatar’s population will be shaped by its ongoing efforts to diversify its economy, improve labor conditions, and foster a more inclusive society for both Qataris and expatriates.
